Roaring Canadian Jobs Market Signals Economic Rebound
Easing Restrictions Ignite Canadian Job Market In February

This morning, Statistics Canada released the February 2021 Labour Force Survey showing much stronger-than-expected job growth. The early days of the latest easing in COVID restrictions reinvigorated the labour market. Economists were pleasantly surprised by the rapid rebound. To be sure, there remain risks to the outlook, a rise in virus cases because of the prevalence of the new variants, but the resilience of the Canadian economy is notable.
Employment rose by 259,200 (1.4%) in February, after falling by 266,000 in the prior two months, nearly reversing the effects of the second pandemic wave. The jobless rate fell a whopping 1.2 percentage points to 8.2%, the lowest rate since the beginning of the pandemic in March 2020.
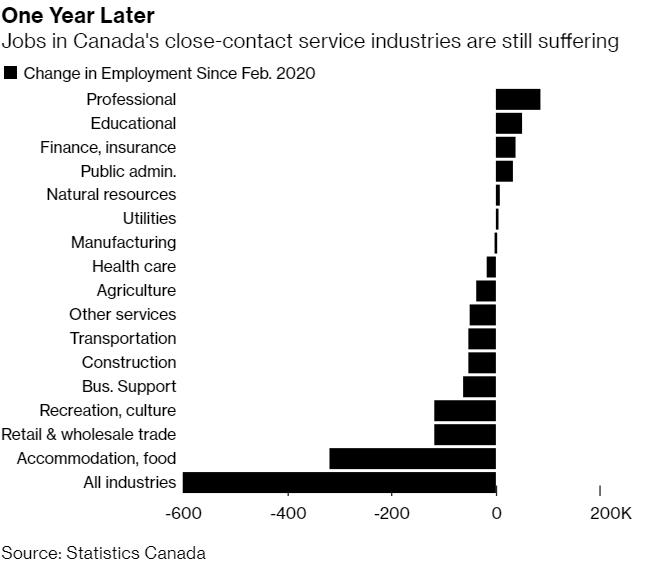
Employment gains in February were concentrated in Quebec and Ontario. Most of the gains in these provinces reflected a rebound in industries—particularly retail trade and accommodation and food services–that had been hardest hit by the lockdowns. Broadly, February’s employment increases were concentrated in lower-waged work. These high-contact service sectors remain among the hardest hit during the crisis (see chart below).
February marked one year of unprecedented pandemic-related changes in the Canadian labour market. Compared with 12 months earlier, there were 599,000 (-3.1%) fewer people employed in February, and 406,000 (+50.0%) more people working less than half of their usual hours. The number of workers affected by the COVID-19 economic shutdown peaked at 5.5 million in April 2020, including a drop in employment of 3.0 million and an increase in COVID-related absences from work of 2.5 million. Since the pandemic began one year ago, there remain over 1 million Canadians who have suffered a loss of employment income.
Pandemic-related changes to the labour market have disproportionately affected young women, particularly teenagers. Compared with February 2020, employment losses among women aged 15 to 24 (-181,000; -14.1%) accounted for nearly one-third (30.2%) of the decline in total employment.
Reflecting a rebound in employment following two months of declines, the number of people on temporary layoff fell by 103,000 (-28.6%) in February. The number of long-term unemployed—those who had been looking for work or been on temporary layoff for 27 weeks or more—fell by 49,000 (-9.7%) from a record high of 512,000 in January.
The number of people who wanted a job but were not actively looking for one and therefore did not meet the definition of unemployed decreased by 33,000 (-5.7%) in February. Had people in this group been included in the unemployment count, the adjusted unemployment rate in February would have been 10.7% (down 1.3 percentage points from January).
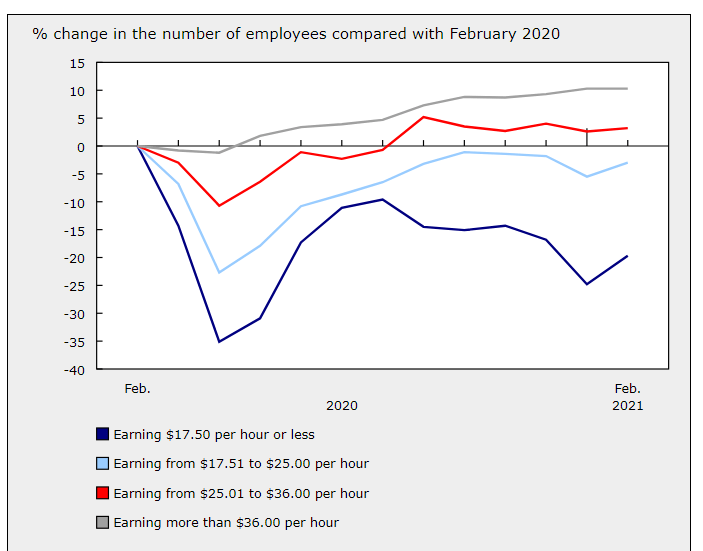
COVID-19 has widened income inequality in Canada, as well as in the rest of the world. By far, the lowest income workers have been hardest hit by the pandemic. We have seen net job gains over the past year for higher-income workers. The following chart sheds light on why the housing market is so strong.
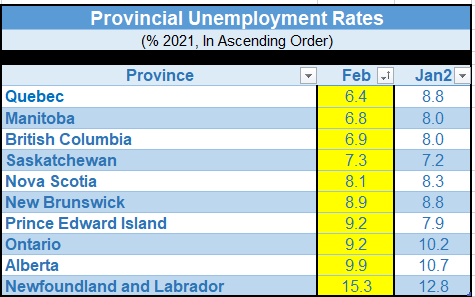
The jobless rate plunged everywhere except Atlantic Canada.
Bottom Line
While Friday’s jobs report surprised on the upside, there are still concerns around an uneven recovery with most of the job losses since last year concentrated in three industries — accommodation and food services, culture and recreation and ‘other services, including personal care. The March employment report may take on even greater importance for the Bank of Canada since it will be the last set of jobs data before the central bank’s April policy decision. Accelerating vaccinations after a slow start would keep the hiring momentum going.
Another strong jobs report combined with recent data showing surprisingly strong growth in Q4 and Q1 economic activity could set the BoC on the road to tapering its bond-buying.
This article was written by DLC's Chief Economist Dr Sherry Cooper and was syndicated with permission.