Record Job Losses, Yet Loonie and Stock Market Rally
Canada Loses over one million jobs in March
Employment in Canada collapsed in March, with over one million jobs lost, wiping away over three years of job creation in a single month and highlighting the economic pain the coronavirus pandemic has swiftly delivered. The decline in jobs in Canada, on a proportional basis, was steeper than in the U.S. The record plunge was anticipated after officials here revealed that in the span of roughly a month, 5 million people, about 20% of the country's labour force, have applied for emergency income support. This reflects Canada's relatively rapid widespread implementation of social distancing.
The sharp increase in unemployment initially caught policymakers by surprise, prompting them to shift their response toward wage subsidies
in order to prevent across-the-board layoffs. About 70% of direct stimulus spending is now targeted at keeping workers on payrolls.
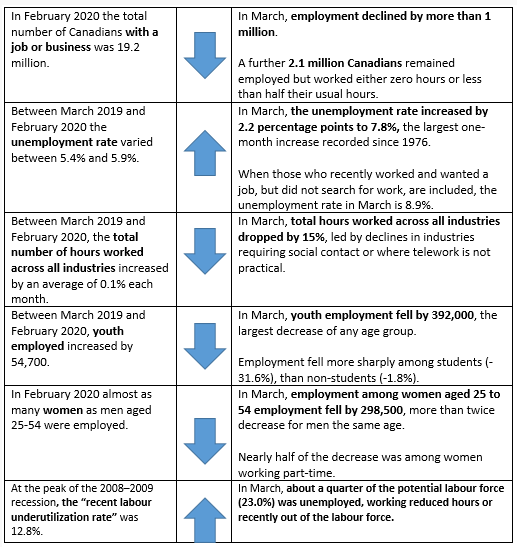
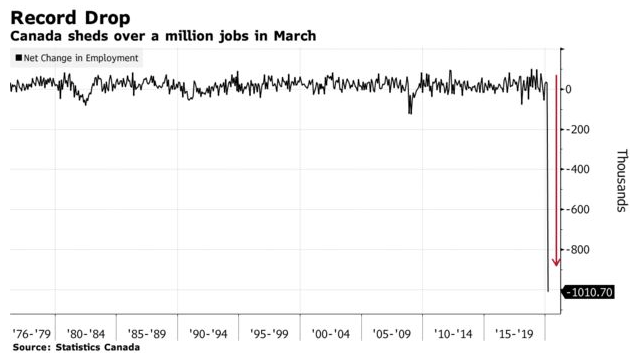
The net number of new jobs plunged by 1.01 million from February, the largest decline in records dating back to 1976
, Statistics Canada said Thursday in Ottawa. The jobless rate surged from 5.6% in February to 7.8% in March.
Actual hours worked declined by 14% from a year ago, and 15% from the previous month, both records.
The March Labour Force Survey ( LFS
) results reflect labour market conditions during the week of March 15 to 21. By then, a sequence of unprecedented government interventions related to COVID-19—including the closure of non-essential businesses, travel restrictions, and public health measures directing Canadians to limit public interactions—had been put in place. These interventions resulted in a dramatic slowdown in economic activity and a sudden shock to the Canadian labour market. today's data might just be a preview of even worse numbers ahead as the economy heads for its deepest downdraft since the Great Depression.
As bad as these numbers are, Statistics Canada said they do not fully measure the size and extent of the impact of COVOD-19 on Canadian workers and businesses. Additional measures are required to do that which include the number of Canadians who kept their job but worked reduced hours, and the number of people who did not look for work because of ongoing business closures. Of those who were employed in March, the number who did not work any hours during the reference week (March 15 to 21) increased by 1.3 million, while the number who worked less than half of their usual hours increased by 800,000. These increases in absences from work can be attributed to COVID-19 and bring the total number of Canadians who were affected by either job loss or reduced hours to 3.1 million.
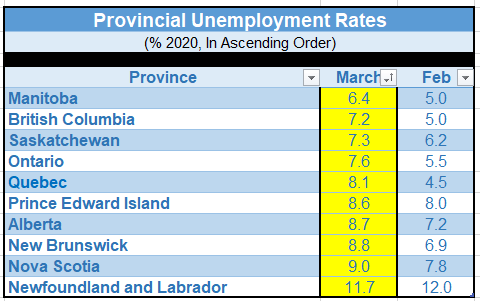
Regionally, employment fell in all provinces, with Ontario (-403,000 or -5.3%), Quebec (-264,000 or -6.0%), British Columbia (-132,000 or -5.2%) and Alberta (-117,000 or -5.0%) the hardest hit.
The unemployment rate increased in all provinces except Newfoundland and Labrador and Prince Edward Island. The largest increases were in Quebec (+3.6 percentage points to 8.1%), British Columbia (+2.2 percentage points to 7.2%) and Ontario (+2.1 percentage points to 7.6%). See the table below for the jobless rate in each province.
In March, the number of people who were out of the labour force—that is, those who were neither employed nor unemployed—increased by 644,000. Of those not in the labour force, 219,000 had worked recently and wanted a job but did not search for one, an increase of 193,000 (+743%). Because they had not looked for work and they were not temporarily laid off, these people are not counted as unemployed. Since historically the number of people in this group is generally very small and stable, the full monthly increase can be reasonably attributed to COVID-19.
Employment decreased more sharply in March among employees in the private sector (-830,200 or -6.7%) than in the public sector (-144,600 or -3.7%).
The number of self-employed workers decreased relatively little in March (-1.2% or -35,900) and was virtually unchanged compared with 12 months earlier. The number of own-account self-employed workers with no employees increased by 1.2% in March (not adjusted for seasonality). Most of this increase was due to an increase in the healthcare and social assistance industry (+16.7%), which offset declines in several other industries. At the onset of a sudden labour market shock, self-employed workers are likely to continue to report an attachment to their business, even as business conditions deteriorate.
The service sector was hardest hit, with almost all of the 1 million decline in employment concentrated in that category. The largest employment declines were recorded in industries that involve public-facing activities or limited ability to work from home. This includes accommodation and food services (-23.9%); information, culture and recreation (-13.3%); educational services (-9.1%); and wholesale and retail trade (-7.2%).
Smaller employment declines were observed in most other sectors, including those related to essential services, such as health care and social assistance (-4.0%). Employment was little changed in public administration; construction; and professional, scientific and technical services. Surprisingly, employment in natural resources rose despite the collapse of oil prices
in March.
Females were also more likely to lose jobs than their male counterparts. Among core-aged workers, female employment dropped more than twice that of men, which might reflect the dominance of males in the construction industry, which was in large measure considered essential work in March. The private sector was responsible for a majority of the losses with employment dropping by 830,200.
Bottom Line:
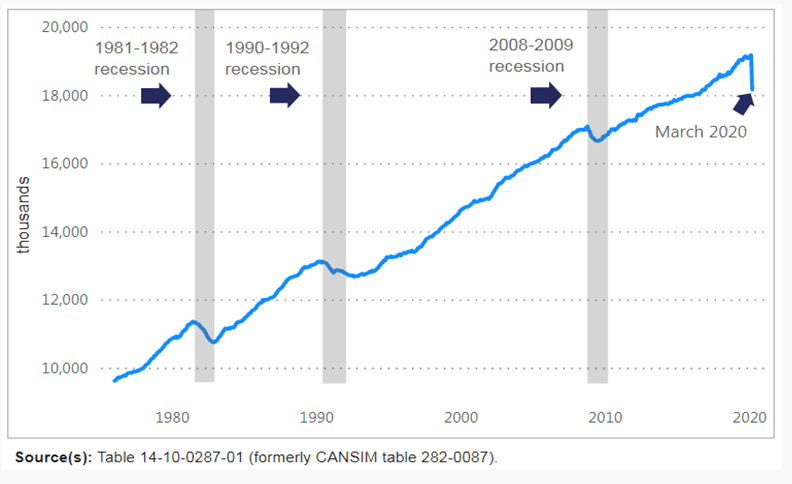
The chart below shows the unprecedented magnitude of the drop in employment last month compared to other recession periods. But this is not your typical recession. This was a government-induced work stoppage to protect us from COVID-19--to flatten the curve of new cases so that our healthcare system could better accommodate the onslaught of critically ill patients. While these are still early days, the data suggests that Canada's early and dramatic nationwide response to the pandemic has been the right thing to do
. We only need to look as near as the United States, where shutdowns were piecemeal, tentative and late. The number of COVID-19 cases is more than 22 times larger in the US than in Canada, while the population is only ten times the size.
To be sure, economic growth in the second quarter will be dismal
. The economists at the Royal Bank
have just posted a forecasted growth rate of an unprecedented -32% in Q2 and a jobless rate rising to 14.6%. They see a bounceback of +20% growth in the third quarter, although it will take until 2022 until Canadian GDP returns to its pre-pandemic level. Underpinning this forecast is the assumption that the economy will be in lockdown for about 12 weeks, with activity only gradually returning to normal after that.
According to the Royal Bank report, "Home resales are expected to fall 20% this year. Job losses, reduced work hours and income, as well as equity-market declines, will keep many buyers out of the market. Governments and banks have policies in place to help owners through this tough patch which should limit forced-selling and a glut of properties coming onto the market. But that doesn’t mean prices won’t come under downward pressure. As in many other industries, we expect the recovery in housing will be gradual. Low interest rates will be a stabilizing force, though it will take a rebound in the labour market as well as a pickup in immigration before sales really accelerate. Our view is that most of the recovery will occur in 2021."
Policymakers have been extremely aggressive in providing income and wage supports. The central bank is unlikely to reduce interest rates below the current overnight rate of 0.25%, but the BoC will continue large-scale purchases of government bonds, mortgage-backed securities (along with CMHC), bankers' acceptances and commercial paper--reducing the cost of funds for the banks and improving liquidity in all markets. " All told, the government support measures add up to 11.5% of GDP making the entire package one of the largest of the developed countries.
"
This article was written by Dr. Sherry Cooper, DLC's Chief Economist. We shared it on our blog because it has lots of great information. Concerned with your financial situation? Give any of our Canadian Mortgage Experts a call anytime.